The Ultimate Guide to Understanding the Difference Between Ethylene Glycol and Propylene Glycol
Introduction
Glycols are versatile compounds widely used across various industries, from automotive to food and pharmaceuticals. Among them, ethylene glycol (EG) and propylene glycol (PG) stand out due to their extensive applications and distinct properties. Understanding the differences between these two glycols is crucial for selecting the appropriate one for specific needs.
Key Takeaways
- Ethylene glycol is best for industrial cooling; propylene glycol is safer for food and cosmetics.
- EG is more cost-effective, PG is more environmentally friendly.
- GZ Industrial Supplies provides food-grade, high-purity glycols with nationwide availability.
Epochem Ethylene Glycol 20 Liters Keg
Chemical Composition and Physical Properties
Ethylene Glycol (EG)
- Chemical Formula: C₂H₆O₂
- Appearance: Colorless, odorless, sweet-tasting liquid
- Boiling Point: Approximately 197.3°C (387°F)
- Freezing Point: Approximately -12.9°C (8.8°F)
- Viscosity: Lower than PG, facilitating better flow in systems
Propylene Glycol (PG)
- Chemical Formula: C₃H₈O₂
- Appearance: Colorless, nearly odorless, slightly sweet-tasting liquid
- Boiling Point: Approximately 188.2°C (370.8°F)
- Freezing Point: Approximately -59°C (-74.2°F)
- Viscosity: Higher than EG, which may affect flow rates in certain applications
Learn more: Comparative Dielectric Study of Ethylene Glycol and Propylene Glycol
Toxicity and Safety Profiles
Ethylene Glycol
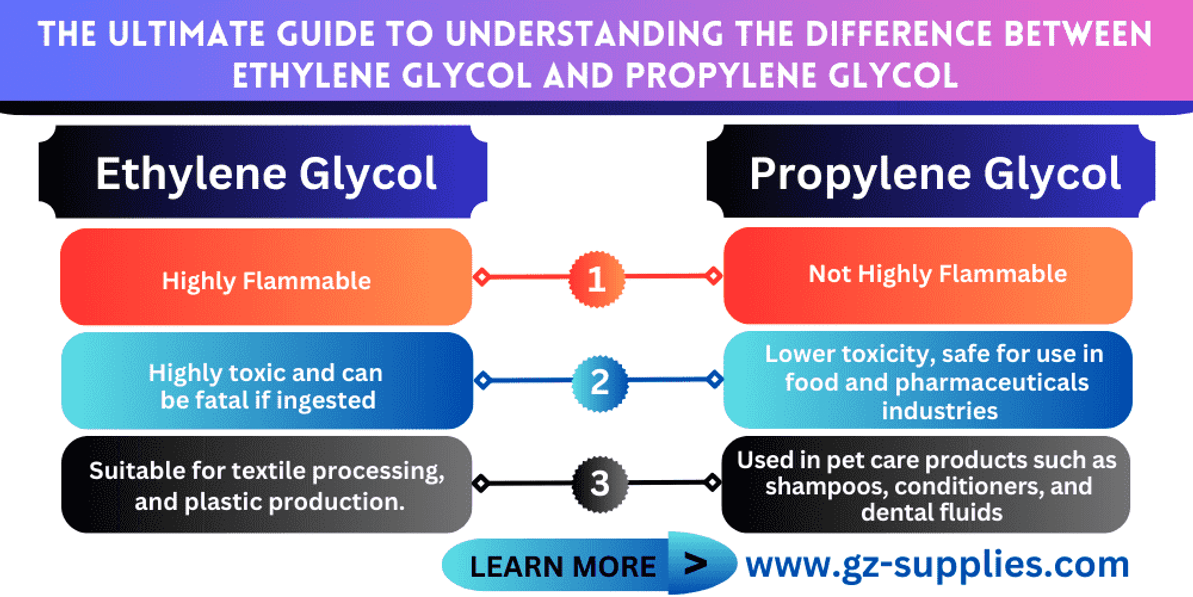
EG is toxic to humans and animals if ingested. Even small amounts can lead to serious health issues, including kidney failure and death. Due to its toxicity, EG should be handled with care, and its use is restricted in applications where accidental ingestion is possible.Byrdie
Propylene Glycol
PG is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. It has a low toxicity profile, making it suitable for applications involving direct human contact or consumption.
Thermal Performance and Efficiency
Ethylene Glycol
EG has superior thermal conductivity and a lower viscosity compared to PG, making it more efficient in heat transfer applications. Its properties allow for effective operation in systems requiring rapid heat dissipation, such as automotive cooling systems.
Propylene Glycol
While PG has a higher viscosity and slightly lower thermal conductivity than EG, it is still effective in heat transfer applications, especially where non-toxicity is a priority. PG is commonly used in systems where human exposure is possible, such as in food processing equipment and HVAC systems in residential settings.
Epochem Propylene Glycol 20 Liters
Common Applications
Ethylene Glycol
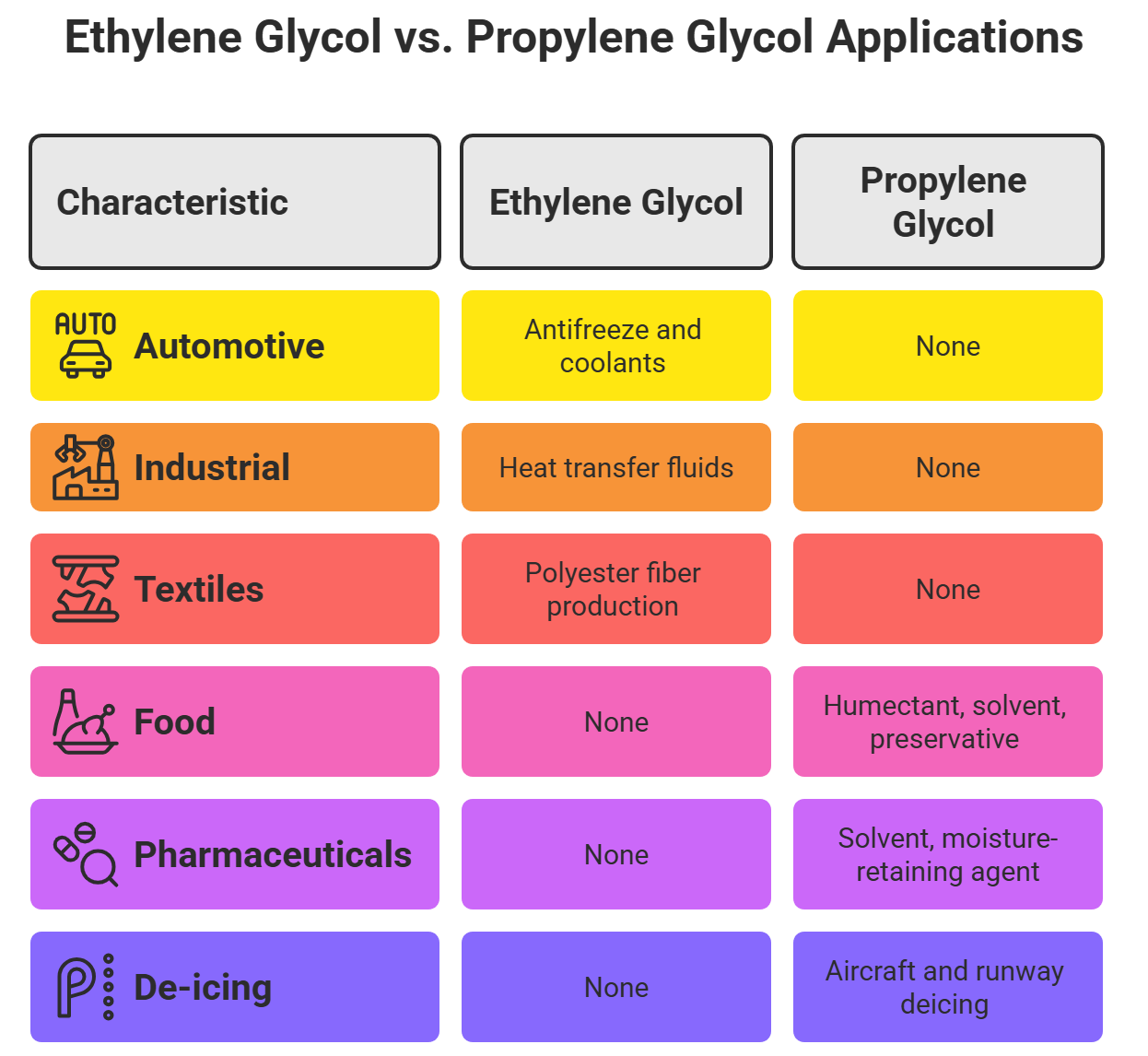
- Automotive Antifreeze and Coolants: EG is a primary component in engine coolants, preventing freezing and overheating.
- Industrial Heat Transfer Fluids: Used in various industrial processes requiring efficient heat exchange.
- Production of Polyester Fibers: EG is a key raw material in manufacturing polyester for textiles and plastics.
Propylene Glycol
- Food Industry: Acts as a humectant, solvent, and preservative in food products.
- Pharmaceuticals and Cosmetics: Used as a solvent and moisture-retaining agent in creams, lotions, and medications.
- De-icing Solutions: Employed in formulations for de-icing aircraft and runways, where low toxicity is essential.
Environmental Considerations
Ethylene Glycol
- Toxic to Aquatic Life: EG can cause environmental damage if released in large quantities.
- Biodegradability: It is biodegradable under specific conditions, but proper disposal is crucial to prevent contamination of water sources.
- Handling Concerns: Due to its toxicity, EG must be stored and transported with strict safety protocols.
Propylene Glycol
- Low Environmental Impact: PG is far less toxic to wildlife and aquatic organisms.
- Biodegradable: It degrades quickly in the environment, making it the preferred option for applications where spills or leaks could occur.
- Sustainable Use: Favored in food and pharmaceutical industries due to its lower ecological footprint.
Cost and Availability
Ethylene Glycol
- More Cost-Effective: Often less expensive than PG, making it a common choice in industrial-scale applications.
- Widespread Availability: Used globally in automotive and industrial sectors.
Propylene Glycol
- Slightly More Expensive: Due to its food- and pharma-grade formulations and higher production standards.
- Available in Various Grades: Including USP (pharmaceutical grade), food grade, and industrial grade.
Regulatory and Industry Standards
Ethylene Glycol:
- Regulated for use in non-ingestible applications.
- Labeling and handling are strictly enforced due to toxicity.
Propylene Glycol:
- Approved by FDA, WHO, and other international bodies for food and drug applications.
- Complies with USP, FCC, JP, and EP standards.
Our Epochem® Propylene Glycol is food-grade and packaged under ideal conditions for safe use across industries.
Comparative Analysis Table
|
Feature |
Ethylene Glycol (EG) |
Propylene Glycol (PG) |
|
Chemical Formula |
C₂H₆O₂ |
C₃H₈O₂ |
|
Toxicity |
High – toxic if ingested |
Low – GRAS status by FDA |
|
Thermal Conductivity |
Higher |
Lower |
|
Viscosity |
Lower |
Higher |
|
Applications |
Automotive, Polyester, HVAC, Plastics |
Food, Pharma, Cosmetics, HVAC, Deicing |
|
Environmental Impact |
Potentially harmful |
Low |
|
Cost |
Lower |
Slightly higher |
|
Safety Use |
Non-consumable use only |
Safe for use in consumables and topicals |
Use Cases and Industry Examples
Industries Using Ethylene Glycol
- Automotive Manufacturing: Used in radiators and anti-freeze formulations for efficient heat dissipation.
- Textile & Plastics Industry: As a raw material in the production of polyester fibers and PET (used in bottles and films).
- Refrigeration Plants: EG is widely used in chiller systems for HVAC and industrial refrigeration.
Industries Using Propylene Glycol
- Food Processing: Acts as a humectant in baked goods and a solvent for food colors and flavors.
- Pharmaceuticals: Used in oral, injectable, and topical medications due to its non-toxic properties.
- Cosmetics: Found in lotions, creams, and deodorants as a moisturizer and solvent.
- Breweries and Beverage Cooling: Propylene glycol is used in food-safe heat transfer fluids.
GZ Industrial Supplies: Your Trusted Glycol Partner in Nigeria
At GZ Industrial Supplies, we offer:
- Epochem® Ethylene Glycol (20L keg): Ideal for industrial coolant and heat transfer applications.
- Epochem® Propylene Glycol (Food Grade): Ideal for food and pharmaceutical industries requiring USP and FCC standards.
Why choose us?
- Trusted quality and packaging
- Food-grade and industrial-grade options
- Nationwide delivery in Nigeria
- Excellent customer support
Propylene Glycol Epochem Brand 215 Liters drum
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I substitute propylene glycol for ethylene glycol in all applications?
Not in all cases. While PG is safer, EG performs better in heat transfer and high-efficiency systems.
2. Is propylene glycol safe for human consumption?
Yes. Our Epochem® PG meets USP and FCC standards, making it safe for food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
3. What is the shelf life of ethylene glycol?
Typically 2-3 years if stored in a cool, dry place in its original container.
4. Can glycol be mixed with water?
Yes, both types can be mixed with water for dilution, especially in cooling systems.
5. Where can I buy glycol in Nigeria?
You can order Epochem® Ethylene Glycol and Propylene Glycol at GZ Industrial Supplies for reliable delivery nationwide.
Conclusion
Whether you're formulating coolants for high-performance engines or looking for a food-safe additive, the choice between ethylene glycol and propylene glycol depends entirely on your specific application. Ethylene glycol delivers superior thermal performance at a lower cost, while propylene glycol stands out for its safety and low environmental impact.
At GZ Industrial Supplies, we stock both Epochem® Ethylene Glycol and Epochem® Propylene Glycol in food-grade packaging under optimal conditions, ensuring purity and safety.
Explore our full glycol range today: GZ Industrial Supplies
Recent Posts
-
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding the Difference Between Ethylene Glycol and Propylene Glycol
Introduction Glycols are versatile compounds widely used across various industries, from automotive …Apr 16, 2025 -
What are Agricultural Machinery
Introduction Agricultural Machinery is also used to improve the wide range of production prac …Apr 14, 2025 -
The Best Electrical Wire in Nigeria 2025 (Updated)
Introduction Electrical wires are the basic unit of every electrical system. Electrical wires …Apr 14, 2025