Top 10 Industrial Hubs in Nigeria: A Guide for Suppliers and Manufacturers
Introduction
Nigeria, Africa's largest economy, boasts a diverse and rapidly growing industrial sector. This growth is anchored by several key industrial hubs spread across the country, each with its unique strengths and specializations. For suppliers and manufacturers looking to tap into Nigeria's vast market potential, understanding these industrial centers is crucial. This comprehensive guide explores the top 10 industrial hubs in Nigeria, providing invaluable insights into their characteristics, key industries, and the opportunities they present.

Magnetic Core Drilling Machine SCY-35HD Cayken
Key Takeaways
- Nigeria's industrial landscape is diverse, with each hub offering unique opportunities and challenges for suppliers and manufacturers.
- The Lagos-Ogun Industrial Axis remains the country's primary industrial center, offering access to large markets and ports but facing infrastructure challenges.
- Port Harcourt specializes in oil and gas industries, while Kano serves as the commercial nucleus for Northern Nigeria with strengths in agro-processing and textiles.
- Emerging hubs like Aba and Akure offer opportunities in small-scale manufacturing and tech-driven industries respectively, showcasing Nigeria's evolving industrial sector.
Criteria for Selecting the Top Industrial Hubs
When selecting the top industrial hubs in Nigeria, several critical factors were considered:
- Economic Contribution: The GDP contribution of each hub, highlighting its importance to the national economy.
- Infrastructure: The availability of key infrastructure such as roads, ports, power supply, and communication networks, which are essential for industrial operations.
- Workforce Availability: The presence of a skilled and unskilled labor force, as well as educational institutions that provide training relevant to industrial needs.
- Market Access: Proximity to major domestic and international markets, ensuring ease of distribution and access to consumers.
Government Policies and Incentives: The presence of favorable government policies, tax incentives, and other support mechanisms that encourage industrial growth in these areas.
1. Lagos-Ogun Industrial Axis: The Economic Powerhouse
The Lagos-Ogun Industrial Axis stands as Nigeria's premier industrial hub, encompassing the bustling metropolis of Lagos and extending into neighboring Ogun State. This region is the beating heart of Nigeria's manufacturing sector, accounting for over 50% of the country's industrial output. The hub's success is built on a foundation of strategic advantages: proximity to Nigeria's busiest seaports, a vast consumer market of over 20 million people in the Lagos metropolitan area, and relatively well-developed infrastructure compared to other parts of the country.
In Lagos, industrial activities are concentrated in areas such as Ikeja, Ilupeju, and Apapa. These zones host a diverse range of industries, from food and beverages to textiles, chemicals, and electronics. The Apapa port complex, despite its congestion challenges, remains a crucial gateway for raw materials and finished products. Ogun State, particularly the Agbara and Ota industrial estates, has seen rapid growth in recent years, attracting major manufacturers with its proximity to Lagos and comparatively lower operating costs.
The Lagos-Ogun axis is particularly attractive to suppliers of industrial machinery, raw materials, and logistics services. The high concentration of manufacturing activities creates a constant demand for equipment maintenance, spare parts, and industrial consumables. However, businesses operating in this hub must navigate challenges such as traffic congestion, high real estate costs, and intermittent power supply. Many companies in the region have invested in private power generation to ensure uninterrupted operations.

Solar Panel (Mono PERC) 390watt Tescom
2. Port Harcourt: The Oil and Gas Hub
Port Harcourt, the capital of Rivers State, is the nucleus of Nigeria's oil and gas industry. This industrial hub's economy revolves around petroleum, with numerous oil and gas companies, refineries, and petrochemical plants dotting its landscape. The presence of two major seaports – the Port Harcourt Port and the Onne Port – further enhances its strategic importance for industries requiring heavy machinery and bulk raw materials.
Beyond oil and gas, Port Harcourt has a growing manufacturing sector, particularly in areas such as metal fabrication, plastics, and food processing. The city's industrial layout, including the Trans-Amadi Industrial Layout, houses a diverse range of factories and workshops. For suppliers, Port Harcourt offers significant opportunities in providing specialized equipment and services to the oil and gas sector, as well as supporting industries.
However, operating in Port Harcourt comes with unique challenges. Security concerns in the wider Niger Delta region can impact business operations, and environmental regulations are particularly stringent due to the ecological sensitivity of the area. Suppliers and manufacturers looking to establish a presence in Port Harcourt must be prepared to navigate these complexities while capitalizing on the hub's strategic advantages.

3. Kano: The Commercial Nucleus of Northern Nigeria
Kano, Nigeria's second-largest city, has been a commercial powerhouse for centuries, serving as a key terminus of trans-Saharan trade routes. Today, it stands as the industrial hub of Northern Nigeria, with a focus on agro-processing, textiles, and leather goods. The Challawa, Bompai, and Sharada industrial estates form the core of Kano's manufacturing sector, hosting hundreds of factories and small-scale industries.
Kano's strategic location makes it a gateway to markets in Nigeria's northern states and neighboring countries like Niger and Chad. The city's long history of commerce has fostered a robust ecosystem of traders, suppliers, and skilled artisans. For manufacturers, Kano offers access to agricultural raw materials from the surrounding region and a large pool of labor.
Suppliers to Kano's industries should be aware of the unique market dynamics of Northern Nigeria. There's a strong demand for machinery and equipment suited for agro-processing and textile manufacturing. Additionally, the leather industry, centered around the famous Kano tanneries, presents opportunities for suppliers of chemicals and specialized equipment.
However, businesses operating in Kano face challenges such as inadequate power supply and occasional security concerns. Many manufacturers have adapted by investing in captive power plants and robust security measures. Despite these challenges, Kano's potential as a manufacturing hub continues to grow, supported by initiatives like the Kano Free Trade Zone.

Stainless Gasoline Grating Machine 6.5hp Hellog
4. Aba: The Hub of Small-Scale Manufacturing
Aba, located in Abia State, is renowned as Nigeria's capital of small-scale manufacturing. This vibrant city is famous for its leather works, garments, and consumer goods production. The Ariaria International Market, one of the largest markets in West Africa, showcases Aba's manufacturing prowess, with thousands of small workshops producing a wide range of goods.
What sets Aba apart is its ecosystem of highly skilled artisans and entrepreneurs. The city has a unique model of clustered production, where groups of specialized workshops collaborate to produce finished goods. This system has made Aba particularly resilient and adaptable to market changes.
For suppliers, Aba presents unique opportunities and challenges. There's a constant demand for raw materials, tools, and small-scale machinery. However, the market is highly price-sensitive, and suppliers need to offer competitive pricing and flexible terms. The informal nature of many businesses in Aba also requires suppliers to develop strong personal relationships and trust with local entrepreneurs.
Manufacturers looking to tap into Aba's potential should consider its strengths in leather goods, textiles, and plastics. The city's skilled workforce and established production networks can be leveraged for contract manufacturing or collaborative ventures. However, infrastructure challenges, particularly in power supply and transportation, remain significant hurdles that businesses must navigate.

Kaierda Inverter Manual Arc Welding Machine (ZX7-630S)
5. Kaduna: The Emerging Industrial Powerhouse of the North
Kaduna, once the industrial heartland of Northern Nigeria, is experiencing a renaissance as a key manufacturing hub. The state government's aggressive industrialization drive, coupled with its strategic location and relatively stable power supply, has attracted significant investments in recent years. The Kaduna Free Trade Zone and the Green Economic Zone are at the forefront of this industrial revival.
Key industries in Kaduna include textiles, food processing, and automobiles. The presence of the Defence Industries Corporation of Nigeria (DICON) has also fostered a growing defense and aerospace industry. For suppliers, Kaduna offers opportunities in providing machinery, raw materials, and services to these diverse sectors.
Kaduna's advantage lies in its relatively lower operating costs compared to Lagos or Port Harcourt, coupled with good rail connectivity to other parts of Nigeria. The state's focus on education and skills development is also creating a pool of skilled labor attractive to manufacturers.
However, businesses operating in Kaduna must be aware of the socio-economic dynamics of the region. Community engagement and corporate social responsibility initiatives are often crucial for smooth operations. Additionally, while security has improved significantly, it remains a consideration for businesses planning long-term investments in the region.

Bosch Automotive and Starter Battery S4 200AH 12Vk
6. Enugu: The Coal City's Industrial Renaissance
Enugu, historically known as the "Coal City" due to its coal mining heritage, is emerging as a significant industrial hub in southeastern Nigeria. While coal mining has declined, Enugu has diversified its industrial base, focusing on sectors such as food processing, building materials, and pharmaceuticals. The 9th Mile Corner area, in particular, has seen significant industrial development in recent years.
Enugu's strategic location, serving as a gateway to other southeastern states, makes it an attractive base for manufacturers looking to serve the regional market. The state has also been proactive in attracting investments, offering incentives through its Investment Promotion Agency.
For suppliers, Enugu presents opportunities in providing equipment and materials for its growing food processing and pharmaceutical industries. The construction boom in the southeast has also driven demand for building materials, creating opportunities for suppliers in this sector.
One of Enugu's unique advantages is its relatively stable power supply, thanks to the Oji River Power Station. However, like many Nigerian cities, Enugu faces challenges in infrastructure development and maintenance. Businesses operating here often need to invest in backup power solutions and may face logistical challenges in moving goods to and from the city.

Used Caterpilla Fork Lift 15 tons for Sale
7. Calabar: The Tourism and Export Processing Hub
Calabar, the capital of Cross River State, has positioned itself as both a tourism destination and an industrial hub, particularly through its Export Processing Zone (EPZ). The Calabar Free Trade Zone, established in 1992, has attracted a diverse range of industries, from food processing to electronics assembly.
Calabar's deep seaport gives it a significant advantage for export-oriented industries. The city has also benefited from relatively better urban planning compared to many Nigerian cities, making it attractive for businesses that value quality of life for their employees.
Key industries in Calabar include pharmaceuticals, food processing, and light manufacturing. The tourism sector, while not strictly industrial, plays a significant role in the local economy and supports a range of associated industries.
Suppliers to Calabar's industries should be aware of the unique requirements of operating within a Free Trade Zone. There are opportunities in providing specialized equipment and materials for the pharmaceutical and food processing industries. The growing tourism sector also creates demand for a range of supplies, from hospitality equipment to construction materials for new hotels and resorts.
However, businesses in Calabar face challenges such as its relative geographic isolation from Nigeria's major economic centers. Transportation costs can be high, and the local market is relatively small compared to hubs like Lagos or Kano. Successful operations in Calabar often require a focus on export markets or serving the broader southeastern region.

Structural Steel 6000 x1500x16mm Steel Plates
8. Onitsha: The Commercial Gateway to Eastern Nigeria
Onitsha, straddling the banks of the River Niger in Anambra State, is one of the largest commercial centers in West Africa. While not traditionally thought of as an industrial hub, Onitsha's massive market and strategic location have fostered a growing manufacturing sector, particularly in consumer goods, plastics, and pharmaceuticals.
The Onitsha Harbor Industrial Layout and the emerging Onitsha Industrial Layout are focal points for manufacturing activities. These areas host a range of industries, from food and beverage production to metal fabrication and electronics assembly.
Onitsha's strength lies in its vast trading network, which extends throughout eastern Nigeria and into neighboring countries. For manufacturers, this presents an opportunity to tap into established distribution channels. Suppliers can benefit from the high concentration of businesses needing raw materials, packaging supplies, and light industrial equipment.
However, operating in Onitsha comes with significant challenges. The city is notorious for its traffic congestion, and infrastructure, particularly power supply, can be unreliable. Many businesses operate their own generators and have developed creative solutions for distribution and logistics.
Despite these challenges, Onitsha's potential as an industrial hub continues to grow. The completion of the Second Niger Bridge and ongoing efforts to revitalize the Onitsha river port are expected to further boost the city's industrial capacity.

Energos 12V-220AH Tubular Battery
9. Jos: The High-Altitude Industrial Enclave
Jos, the capital of Plateau State, offers a unique proposition as an industrial hub. Located on the Jos Plateau at an altitude of about 1,238 meters, the city benefits from a temperate climate that sets it apart from much of Nigeria. This climate has historically made Jos a center for agriculture, particularly the cultivation of vegetables and flowers.
In recent years, Jos has been working to diversify its industrial base. The Jos Industrial Layout hosts a range of light industries, including food processing, beverages, and mineral processing. The city's history of tin mining has also left it with a legacy of metalworking skills that continue to be relevant in various manufacturing sectors.
For suppliers, Jos presents opportunities in providing agricultural inputs, food processing equipment, and mining-related supplies. The city's growing tourism sector also creates demand for hospitality-related goods and services.
One of Jos's unique advantages is its potential for high-value agriculture and horticulture. The cool climate allows for the cultivation of crops that are difficult to grow in other parts of Nigeria, creating opportunities for agro-processing industries.
However, businesses operating in Jos must navigate challenges such as occasional security concerns and the city's relative isolation from major economic centers. Transportation costs can be high, and the local market is relatively small. Successful businesses in Jos often focus on high-value, low-volume products that can justify the transportation costs to larger markets.

10. Akure: The Emerging Tech and Agro-Industrial Hub
Akure, the capital of Ondo State, is rapidly emerging as a hub for technology and agro-industry. The city's transformation is being driven by a combination of government initiatives, private sector investments, and the presence of the Federal University of Technology, Akure (FUTA).
The Akure Tech Hub, a government initiative, is fostering a growing ecosystem of tech startups and digital service providers. This is complemented by the Ondo-Linyi Industrial Hub, which focuses on light manufacturing, particularly in wood processing and agro-allied industries.
Akure's strengths lie in its educated workforce, relatively low operating costs, and the abundance of agricultural raw materials from the surrounding region. The city is becoming known for its cocoa processing facilities, as Ondo State is one of Nigeria's largest cocoa producers.
For suppliers, Akure offers opportunities in providing agricultural inputs, food processing equipment, and technology-related supplies. The growing tech sector is creating demand for computer hardware, networking equipment, and other IT-related supplies.
However, like many emerging industrial hubs, Akure faces challenges in infrastructure development. Power supply can be inconsistent, and transportation links to major markets need improvement. Businesses operating in Akure often need to be self-reliant in terms of power generation and may face logistical challenges in moving goods to larger markets.
Despite these challenges, Akure's potential as an industrial hub is significant. The combination of technology focus and agro-industrial base positions the city well for future growth, particularly in high-value agricultural processing and digital services.

Nigeria’s Top 10 Industrial Hubs: Key Opportunities for Suppliers and Manufacturers
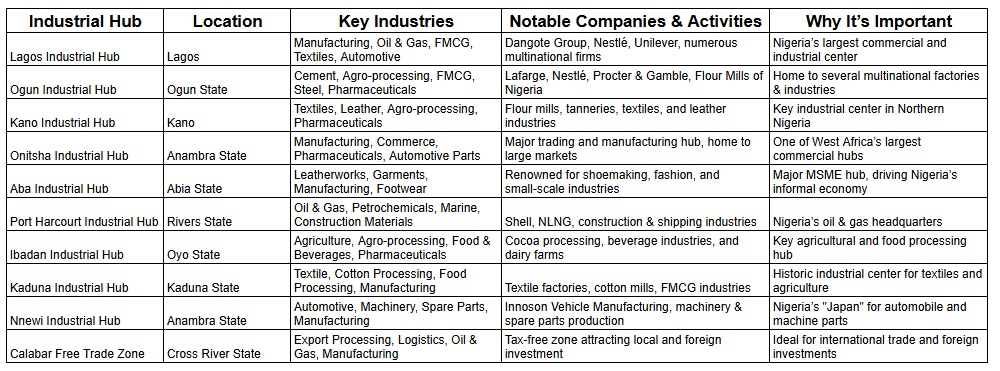
Key considerations for businesses operating across these hubs include:
- Infrastructure resilience: Investing in backup power solutions and robust supply chain management to navigate infrastructure challenges.
- Local partnerships: Developing strong relationships with local businesses and communities to navigate regional dynamics and access market knowledge.
- Regulatory compliance: Staying abreast of both national and state-level regulations, which can vary significantly across different regions.
- Workforce development: Investing in training and skills development to leverage the local workforce effectively.
- Market adaptation: Tailoring products and services to meet the specific needs and preferences of each regional market.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the five major industrial areas in Nigeria?
The five major industrial areas in Nigeria include the Lagos-Abeokuta-Ibadan-Osogbo Zone, known for manufacturing and commercial activities. The Benin-Sapele-Warri Zone is a hub for oil refining and petrochemical industries. The Kaduna-Kano-Jos Zone is recognized for textile production, agriculture, and manufacturing. The Onitsha-Enugu-Owerri-Port Harcourt Zone plays a significant role in trade, transport, and industrial production. Lastly, Abuja and its surrounding industrial clusters are emerging as key centers for various industries, including construction and services.
2. Which industry is best for startups?
The best industries for startups in 2024 include green energy solutions, which focus on renewable energy and sustainability. The health and wellness sector continues to grow with demand for fitness, mental health, and nutrition services. EdTech and online learning offer opportunities for digital education platforms, while generative AI is revolutionizing multiple industries. The food and beverage industry remains profitable with innovative food tech solutions, and cybersecurity is in high demand due to rising digital threats. Additionally, sustainable fashion presents a growing market for eco-friendly clothing and ethical production.
3. What are the key industries in Nigeria's major industrial hubs?
Nigeria's industrial hubs specialize in various sectors, including oil and gas, manufacturing, textiles, agro-processing, and technology. Cities like Lagos and Port Harcourt focus on oil and trade, while Kano and Aba are known for textiles and manufacturing.
4. Why should suppliers and manufacturers consider Nigeria's industrial hubs?
Nigeria's industrial zones offer access to large consumer markets, well-established infrastructure, and government incentives for businesses. These hubs also provide proximity to raw materials and key transportation networks, making them ideal for production and distribution.
5. Which industrial hub in Nigeria is best for setting up a manufacturing business?
The choice depends on the industry. Lagos is ideal for import-export businesses, Ogun and Aba are strong in manufacturing, Kano is excellent for textiles and agriculture, and Port Harcourt is a prime location for oil and gas operations.
Related Articles
Face shield suppliers and distributors in Nigeria
Top 10 Paint Sprayers in Nigeria for Industrial Applications
Conclusion
Nigeria's industrial hubs play a vital role in driving economic growth, providing opportunities for suppliers, manufacturers, and investors. From Lagos to Kano, these regions are strategically positioned to support various industries, including manufacturing, oil & gas, agriculture, and technology. Whether you are looking to expand your business, source raw materials, or establish a production facility, understanding these hubs is essential for success.
Ready to connect with top suppliers and manufacturers in Nigeria’s leading industrial hubs? Visit GZ Industrial Supplies today to explore high-quality industrial products and solutions tailored to your business needs!







