What is the Difference Between 11KV and 33KV Power Transformer Lines?
Introduction
As an electrical engineer or utility professional, you likely handle a variety of power transformer lines on a regular basis. Two of the most common voltage classes for power distribution are 11 kilovolts (11KV) and 33 kilovolts (33KV). While both are essential for transmitting electricity over moderate distances to end users, there are several key differences between these two transformer line types you should understand. Knowing the distinction between 11KV and 33KV power lines can help ensure you properly select, install, and maintain the right transformer system for your application and avoid issues like overloading the lines or causing power outages.
Read more...What are Power Transformer Voltage Ratings
Key Takeaway:
Understanding the differences between 11KV and 33KV power transformer lines is crucial for grasping the nuances of energy transmission. The variance in voltage levels impacts efficiency, capacity, and system design, influencing how electricity is distributed across networks. This knowledge empowers professionals in the electrical engineering field to make informed decisions regarding power distribution and infrastructure upgrades.
Buy Online... Epochem premium Transformer Oil 20 liters
Understanding Power Transformers and Their Role in Electricity Distribution
Power transformers are vital components in any electrical distribution system. They are used to raise or lower voltage levels to facilitate the efficient transmission of electricity over long distances.
The two most common classes of power transformers used by utility companies are 11 kilovolt (11kV) and 33 kilovolt (33kV) transformers. 11kV transformers are typically used for power distribution in residential areas. They step down higher voltage levels to 11,000 volts for delivery to homes and businesses. 33kV transformers are employed for both power transmission and distribution over longer distances. They are used to step up voltage from power plants to 33,000 volts for transmission via power lines.
There are a few key differences between 11kV and 33kV power transformers:
- Voltage Rating: 11kV transformers are rated for 11,000 volts, while 33kV transformers are rated for 33,000 volts. The higher voltage rating of 33kV transformers allows for lower power loss over longer transmission distances.
- Capacity: 33kV transformers typically have a higher capacity, often 10 megavolts-amperes (MVA) or more, compared to 1-5 MVA for most 11kV transformers. The greater capacity of 33kV transformers is necessary to handle the higher power levels required for long distance transmission.
- Cost: 33kV power transformers are more expensive, often costing several million dollars, due to their larger size, higher voltage rating, and more complex design. 11kV transformers are more affordable, ranging from $50,000 up to $500,000.
- Use: 11kV transformers are primarily used for power distribution to end users, while 33kV transformers serve the dual purpose of power transmission over long distances and distribution to large commercial centers or industrial areas with high demand.
In summary, while 11kV and 33kV power transformers perform the same basic function of altering voltage levels, they differ significantly in terms of their voltage rating, capacity, cost, and usage within the power grid. Understanding these distinctions is important for utility planning and ensuring the efficient delivery of electricity.
Read more...What are the six different types of electrical power transformers
Buy Online... Power Transformer 100KVA 11.0/415KV Astor
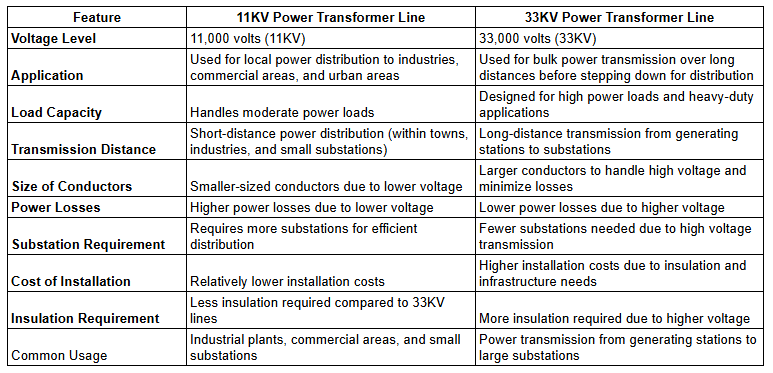
Comparison of 11KV vs. 33KV Power Transformer Lines
Key Differences Between 11KV and 33KV Power Transformers
When selecting power transformers for large-scale electrical power transmission, it is important to understand the key differences between 11 kilovolt (KV) and 33KV options.
Higher Voltage Capacity
33KV power transformers are capable of handling a much higher voltage capacity compared to 11KV transformers. 33KV transformers are typically used for medium- to high-voltage power transmission over long distances, while 11KV transformers are more suitable for distribution to end users.
Size and Cost Differences
33KV power transformers are significantly larger in size and higher in cost compared to 11KV transformers. The larger size is required to properly insulate and cool the transformer at the higher voltage. The increased cost is a result of the more complex design and higher quality materials needed.
Application and Installation
33KV power transformers are commonly used in power transmission substations to step-down high-voltage transmission to distribution levels. 11KV transformers are more often used in distribution substations and on utility poles to further step-down voltage for supplying end users. Installing a 33KV transformer requires more space and a concrete foundation, while 11KV transformers can be pole-mounted.
Efficiency
While 33KV power transformers are well-suited for high-volume, long-distance power transmission, they do result in greater energy losses compared to 11KV transformers over the same distance. The higher the voltage, the lower the current required to transmit the same amount of power, but the larger the transformer the greater the energy losses. Choosing the right voltage for your application can help maximize efficiency.
In summary, the main differences between 11KV and 33KV power transformers are their voltage capacities, sizes, costs, applications, installation requirements, and energy efficiencies. Understanding these key differences will help in selecting a transformer suitable for your needs.
Read more...How to service a power transformer
Buy Online... Power Transformer 100KVA 33/0.415KV
11KV Power Transformers: Ideal for Residential and Commercial Use
11KV power transformers are ideal for powering residential neighborhoods and commercial buildings. These medium-voltage transformers step down high-voltage power from transmission lines to a level suitable for distribution to end users.
Components and Functions
The 11KV power transformer consists of windings, a core, tap changers, cooling radiators, and a tank. The windings are coils of wire that step down the voltage. The core is constructed of laminated steel plates and provides a path for the magnetic flux. Tap changers are devices that can adjust the voltage ratio to accommodate varying loads. Cooling radiators help dissipate the heat generated by the transformer. Finally, the tank contains insulating oil that cools and insulates the windings and core.
Advantages
11KV power transformers offer several benefits for residential and commercial use. They enable the efficient transmission of electric power over medium distances. The lower voltage is safer for end users to handle and less likely to cause dangerous electric arcs. In addition, 11KV transformers require smaller and less expensive distribution lines and equipment. The moderate size and weight of 11KV transformers also make them easier to install and replace compared to higher-voltage models.
Disadvantages
However, there are some downsides to 11KV power transformers. They can only distribute power over limited areas, so more transformers are needed to serve large loads. The lower voltage also results in higher line losses during transmission compared to higher-voltage systems. More frequent tap changing may be required to regulate the voltage for varying loads. Furthermore, the insulation and cooling requirements are still substantial for 11KV class transformers, so they are expensive, bulky pieces of equipment.
11KV power transformers strike a good balance for residential and commercial power distribution with their moderately high voltage, safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. By understanding their components, functions, advantages, and disadvantages, you can determine if 11KV transformers are the right choice for your application.
Buy Online... Power Transformer ABB 50KVA 11.00/0.415KV
33KV Power Transformers: Well-Suited for Heavy-Duty Industrial Applications
33KV power transformers are ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications that require high voltage power. They are capable of handling higher loads and providing more power over greater distances compared to standard 11KV power lines.
Higher Voltage Means More Power
The higher voltage of 33KV power transformers allows them to carry more power over the same size wire. This is because power (P) depends on both voltage (V) and current (I) according to the formula: P=VI. At a higher voltage, the current can be lower while still transmitting the same amount of power. Lower current means less power is lost as heat during transmission.
Longer Transmission Distances
The higher operating voltage of 33KV power transformers also allows electricity to be transmitted over much longer distances. This is because higher voltage power lines encounter less resistance, so less power is lost over the length of the line. 33KV power can be transmitted up to 50-100 miles, while 11KV is only suitable for up to 5-10 miles.
Handles Higher Power Loads
33KV power transformers are built to handle higher power loads, typically 1-50 MVA, compared to 11KV transformers which are usually sized for loads under 10 MVA. The higher voltage and heavier-duty components allow 33KV transformers to power larger facilities and equipment.
Applications
Typical applications of 33KV power include:
- Powering industrial facilities like factories, mills and refineries
- Powering infrastructure like water treatment plants, sewage plants and pumping stations
- Feeding power to 11KV distribution networks in large areas
- Connecting renewable energy generation like solar and wind farms to the main grid
In summary, 33KV power transformers are the preferable choice for any application where high amounts of power need to be transmitted over long distances or used to supply heavy power loads. Their higher voltage and more robust design make them suitable for the demanding needs of industrial and utility customers.
Buy Online... ABB Power Transformer 50KVA 33/0.415KV
Choosing Between 11KV and 33KV Power Transformers for Your Needs
Choosing between 11KV and 33KV power transformers depends on several factors relating to your specific needs and usage requirements.
11KV power transformers are best suited for lower-demand residential and commercial applications. They are capable of handling loads up to 5 MVA and voltages up to 12 kV. 11KV transformers are more compact, lightweight, and affordable. They require less space for installation and have lower upfront costs. However, their lower capacity means they may need to be replaced more frequently to meet increasing demand.
On the other hand, 33KV power transformers are ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications with high power requirements. They can handle 10 MVA or greater and voltages up to 36 kV. Although 33KV transformers are larger in size and more expensive, they provide significantly more capacity and a longer service life. The higher voltage enables electricity to be transmitted over longer distances with less power loss.
Cost Considerations
The initial purchase price and installation costs are generally higher for 33KV power transformers versus 11KV models. However, 33KV transformers may have a lower cost per kVA and prove more economical in the long run due to their extended lifespan and reduced energy losses. The specific costs in your area will depend on factors like raw material prices, labor rates, and utility company fees. You should compare quotes from multiple suppliers to find the most affordable option that suits your needs.
In summary, 11KV power transformers are best for lower-demand uses where compact size and lower upfront cost are priorities, while 33KV models are preferable for heavy-duty industrial applications that require greater capacity and power efficiency. By evaluating your current and future needs, you can determine which voltage level is right for your purposes.
Buy Online... Power Transformer ABB 500KVA 33.0/415KV
Frequently Asked Question
1. What is the 11 kV power line?
An 11 kV power line is a medium-voltage transmission line used for distributing electricity from substations to smaller transformers before reaching end users. It is commonly found in industrial, commercial, and rural power distribution networks, featuring heavy-duty construction for reliable operation in harsh conditions.
2. What is a 33 kV line?
A 33 kV power line is a medium-voltage transmission line designed to operate at 33,000 volts. It is commonly used for power distribution in industrial areas, large commercial setups, and rural electrification. While many regions follow IEC standards (IEC 60502-2), some countries still use British Standards for this voltage rating.
3. Why is transmission line voltage 11 kV, 33 kV, or 66 kV?
Related Articles
Where to Buy Power Transformers in Nigeria
Get Your High Quality Power Transformers Online
Why Transformer oils are needed in Transformer Maintenance
The Best Transformer prices in Nigeria - GZ Industrial Supplies
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between 11KV and 33KV power transformer lines is crucial for selecting the right power distribution system. While 11KV lines are best suited for localized distribution, 33KV lines are ideal for long-distance transmission and industrial applications. Choosing the right transformer setup enhances efficiency, minimizes power losses, and ensures a reliable power supply.
Need high-quality transformers and electrical solutions? Visit GZ Industrial Supplies today to explore our premium range of power transformers and electrical components designed to meet your energy needs!
Recent Posts
-
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding the Difference Between Ethylene Glycol and Propylene Glycol
Introduction Glycols are versatile compounds widely used across various industries, from automotive …Apr 16, 2025 -
What are Agricultural Machinery
Introduction Agricultural Machinery is also used to improve the wide range of production prac …Apr 14, 2025 -
The Best Electrical Wire in Nigeria 2025 (Updated)
Introduction Electrical wires are the basic unit of every electrical system. Electrical wires …Apr 14, 2025